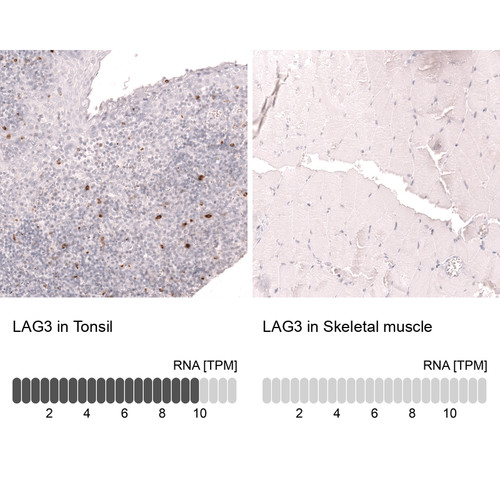
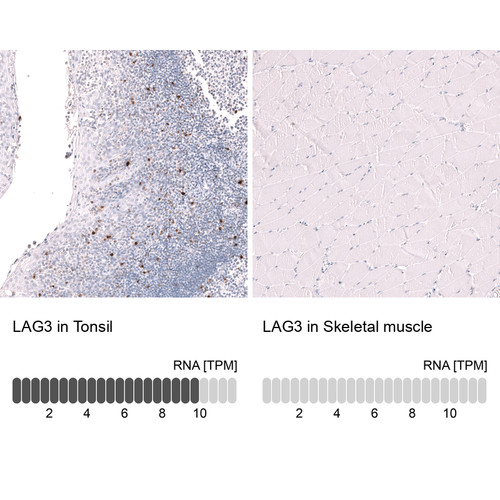
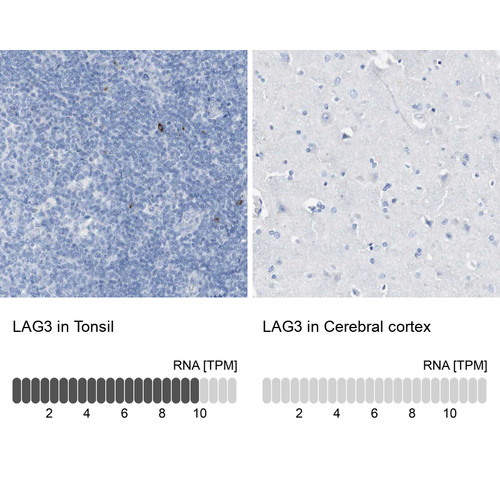
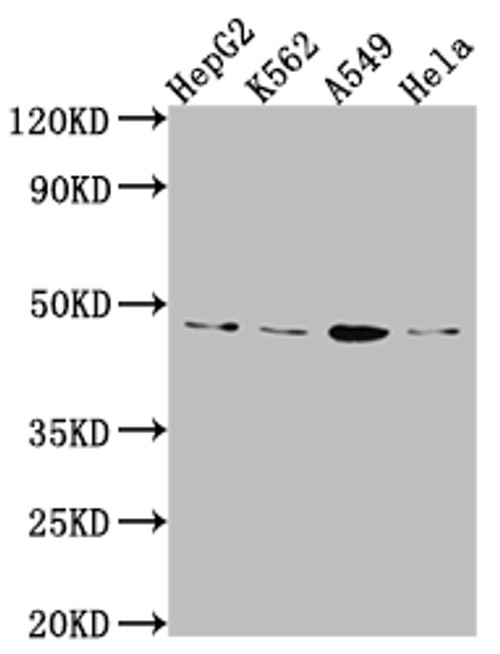
T cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a central role in the adaptive immune system, responsible for recognizing and responding to specific antigens. They originate in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus, where they differentiate into various subsets, including helper T cells (CD4+), cytotoxic T cells (CD8+), and regulatory T cells. Helper T cells coordinate immune responses by activating other immune cells, cytotoxic T cells kill infected or cancerous cells, and regulatory T cells help maintain immune tolerance to prevent autoimmunity. T cells recognize antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules on the surface of other cells, enabling precise targeting of pathogens or abnormal cells.
View our collection of reagents for the study of T cells below.