 CAC Antibody Collection
CAC Antibody Collection
The antibodies on this page are part of Cosmo Bio's exclusive CAC Collection. For many many thousands of other antibodies from many different makers, use our Search the Store function and our Explore Products drop down menu.
Transporters
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Research has correlated defects in specific carrier proteins with specific diseases. A membrane transport protein (or simply transporter) is a membrane protein that acts as such a carrier. [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2019, May 9). Transport protein. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:43, June 6, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transport_protein&oldid=896329420]
| Product name (click for order info) | Cat No (click for datasheet) |
Host | Species specificity |
| Anti Solute Carrier Family 2, Facilitated Glucose Transporter Member 2 (GLUT-2) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) | CAC-TNL-003-GL2 | RAB | MS RT |
| Anti Monocarboxylate transporter 2 (MCT2) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) | CAC-YCU-M-MCT2A | RAB | MS |
| Product name | Anti Solute Carrier Family 2, Facilitated Glucose Transporter Member 2 (GLUT-2) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) |
| Cat No | CAC-TNL-003-GL2 |
| Description | Glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) also known as solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2 (SLC2A2) is a transmembrane carrier protein that enables protein facilitated glucose movement across cell membranes. It is the principal transporter for transfer of glucose between liver and blood. Unlike GLUT4, it does not rely on insulin for facilitated diffusion. GLUT2 has high capacity for glucose but low affinity (high Km, ca. 15-20 mM) and thus functions as part of the "glucose sensor" in the pancreatic β-cells of rodents, though in human β-cells the role of GLUT2 seems to be a minor one. It is a very efficient carrier for glucose.GLUT2 also carries glucosamine. When the glucose concentration in the lumen of the small intestine goes above 30 mM, such as occurs in the fed-state, GLUT2 is up-regulated at the brush border membrane, enhancing the capacity of glucose transport. Basolateral GLUT2 in enterocytes also aids in the transport of fructose into the bloodstream through glucose-dependent cotransport. References: 1) Thorens B, Cheng ZQ, Brown D, Lodish HF. (1990) Liver glucose transporter: a basolateral protein in hepatocytes and intestine and kidney cells. J Am Physiol. 259(2 Pt 1):C279-85. |
| Host | RAB |
| Species specificity | MS RT |
| Product name | Anti Monocarboxylate transporter 2 (MCT2) pAb (Rabbit, Antiserum) |
| Cat No | CAC-YCU-M-MCT2A |
| Description | MCT2 is a proton-coupled monocarboxylate transporter is encoded in humans by the SLC16A7 gene. It catalyzes the rapid transport across the plasma membrane of many monocarboxylates such as lactate, branched-chain oxo acids derived from leucine, valine and isoleucine, and the ketone bodies acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate. It also functions as high-affinity pyruvate transporter. Both Northern blot analysis and inspection of the human expressed sequence tag (EST) database suggest relatively little expression of MCT2 in human tissues. As well, the sequence of MCT2 is far less conserved across species than that of MCT1 or MCT4 and there also appear to be considerable species differences in the tissue expression profile of this isoform. Of the four known mammalian lactate transporters (MCTs 1-4), MCT2 harbors the highest affinity for lactate. In parallel, MCT2 gene transcription has been demonstrated to respond with high-sensitivity to hypoxia, intracellular pH, and, to lactate. [from: Wikipedia contributors. (2019, April 20). Monocarboxylate transporter 2. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:41, June 6, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Monocarboxylate_transporter_2&oldid=893305296] References: 1) Watanabe-Kaneko K, et al. (2007) The synaptic scaffolding protein Delphilin interacts with monocarboxylate transporter 2. Neuroreport. 18(5):489-493. |
| Host | RAB |
| Species specificity | MS |
| Figure 1 | 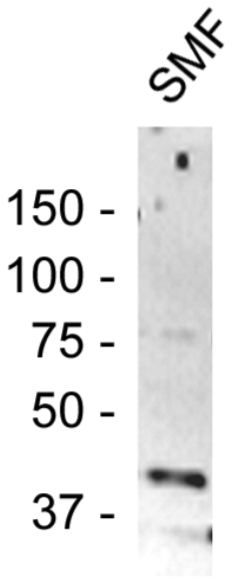 |
| Immunoblot analysis of Anti monocarboxylate transporter 2 (MCT2) on mouse cerebellum synaptic membrane extract. Mouse cerebellum synaptic membrane fraction (SMF) was resolved by electrophoresis, transferred to PVDF and probed with anti-mouse monocarboxylate transporter 2 antibody. Antibody-bound proteins were visualized using HRP-goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody and a chemiluminescence detection system. | |
