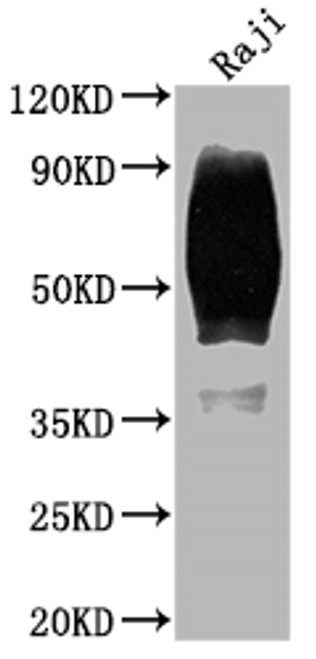
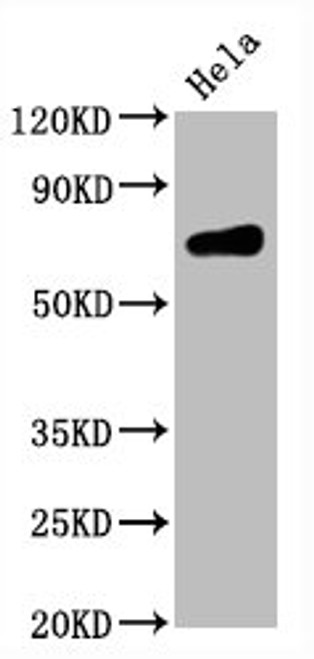
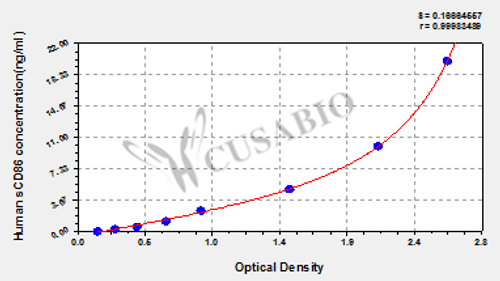
B cells are a type of white blood cell essential to the adaptive immune system, responsible for producing antibodies that help neutralize pathogens. Originating and maturing in the bone marrow, B cells play a critical role in humoral immunity by recognizing specific antigens through their surface immunoglobulin receptors. Upon activation by an antigen and signals from helper T cells, they differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibodies or memory B cells that provide long-term immunity. B cells also contribute to antigen presentation and cytokine secretion, bridging innate and adaptive immunity.
View our collection of reagents for the study of B cells below.