BACKGROUND
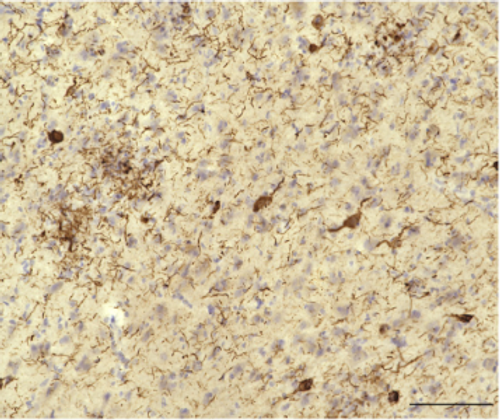
Tau was first reported as a microtubule-associated protein (MAP), named after the Greek letter τ (tau), due to its function as a heat-stable protein essential for microtubule assembly. Normally, tau is primarily localized in the axons of neurons. However, in Alzheimer’s disease and many other neurodegenerative disorders, hyperphosphorylated or ubiquitinated tau accumulates and forms fibrillary aggregates in cell bodies, dendrites, and axons. The distribution pattern and packing density of tau aggregates are closely correlated with neuropathological staging.
Although there is only a single tau gene, alternative splicing produces multiple isoforms; six tau isoforms have been identified in the adult human brain. Within the central to the C-terminal region of tau, there are 31–32 amino acid repeat sequences. In adult humans, the 3-repeat (3R) and 4-repeat (4R) tau isoforms are expressed in roughly equal abundance. Interestingly, in Alzheimer’s disease, both 3R and 4R tau form fibrillar, phosphorylated aggregates in roughly similar amounts, whereas in Pick’s disease, 3R tau predominates in affected neurons; in corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), 4R tau is the predominant aggregated form in neurons and glial cells.
Because abnormal tau aggregation is observed in many diseases, it was once thought to be merely a byproduct of disease progression. However, with the discovery of tau gene mutations in frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17), it became clear that tau abnormalities can themselves cause neurodegenerative disease. Experimental evidence now supports a prion-like mechanism of intracellular transmission of pathological tau, which has attracted increasing attention as a possible pathogenic and propagation mechanism in neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease.
Recently, the structures of aggregated tau forms found in Alzheimer’s disease (e.g. paired helical filaments, straight filaments) have been elucidated using cryo-EM methods.
| Product Specifications | |
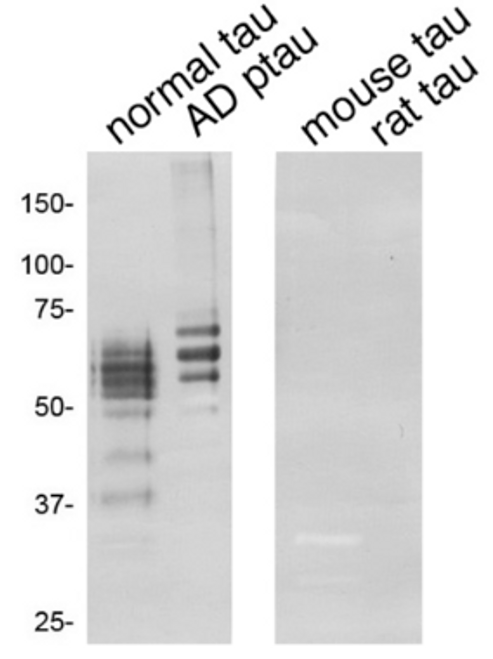
| Application | IF, IP, WB |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Documents & Links for Anti Tau-N pAb | |
| Datasheet | Anti Tau-N pAb Datasheet |
| Flyer | Anti Tau-N pAb Flyer |
| Documents & Links for Anti Tau-N pAb | |
| Datasheet | Anti Tau-N pAb Datasheet |
| Flyer | Anti Tau-N pAb Flyer |