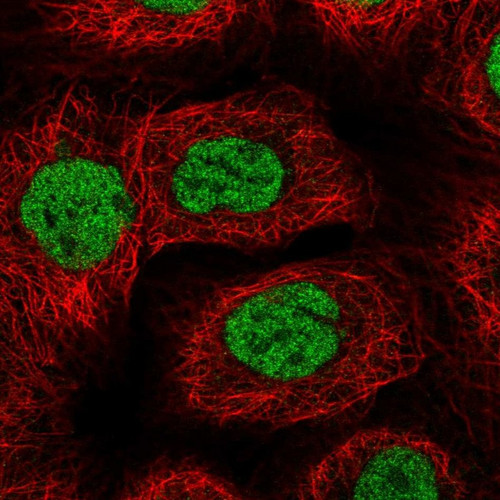
Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949)
Atlas Antibodies
- Catalog No.:
- ATL-HPA034949-25
- Shipping:
- Calculated at Checkout
$423.00
Gene Name: BACH1
Alternative Gene Name: BACH-1, BTBD24
Isotype: IgG
Interspecies mouse/rat: ENSMUSG00000025612: 97%, ENSRNOG00000001582: 96%
Entrez Gene ID: 571
Uniprot ID: O14867
Buffer: 40% glycerol and PBS (pH 7.2). 0.02% sodium azide is added as preservative.
Storage Temperature: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
| Product Specifications | |
| Application | ICC, IHC, ChIP-Exo-Seq |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen | LGIRISESPEPGQRTFTTLSSVNCPFISTLSTEGCSSNLEIGNDDYVSEPQQEPCPYACVISLGDDSETDTEGDSESCSAREQECEVKLPFNAQRIIS |
| Gene Sequence | LGIRISESPEPGQRTFTTLSSVNCPFISTLSTEGCSSNLEIGNDDYVSEPQQEPCPYACVISLGDDSETDTEGDSESCSAREQECEVKLPFNAQRIIS |
| Gene ID - Mouse | ENSMUSG00000025612 |
| Gene ID - Rat | ENSRNOG00000001582 |
| Buffer | 40% glycerol and PBS (pH 7.2). 0.02% sodium azide is added as preservative. |
| Documents & Links for Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) | |
| Datasheet | Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) Datasheet (External Link) |
| Vendor Page | Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) at Atlas Antibodies |
| Documents & Links for Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) | |
| Datasheet | Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) Datasheet (External Link) |
| Vendor Page | Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) |
| Citations for Anti BACH1 pAb (ATL-HPA034949) – 1 Found |
| Takemoto, Kenshiro; Kobatake, Kohei; Miura, Kento; Fukushima, Takafumi; Babasaki, Takashi; Miyamoto, Shunsuke; Sekino, Yohei; Kitano, Hiroyuki; Goto, Keisuke; Ikeda, Kenichiro; Hieda, Keisuke; Hayashi, Tetsutaro; Hinata, Nobuyuki; Kaminuma, Osamu. BACH1 promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by upregulating oxidative stress-related tumorigenicity. Cancer Science. 2023;114(2):436-448. PubMed |