Other related information: Lectins and Sugar chains
What are Lectins?
Lectin is defined by Goldstein 1) et al. As follows.
- A glyco-binding protein or glycoprotein other than the product of an immune response that aggregates cells or complex carbohydrates.
- It has two or more binding sites and can aggregate animal and plant cells.
- Aggregation is specifically blocked by monosaccharides or oligosaccharides. Generally, lectin is used as a general term for substances having specific binding activity to sugar among proteins or glycoproteins existing in plants, animals, microorganisms, etc.
References
1) Goldstein, IJ, Hughes, RC, Monsigny, M., Osawa, T., and Sharon, N., Nature.285,66 (1980)
Classification of lectins
1957 O.D. Mäkelä classified them into four groups according to the coordination of hydroxyl groups at the C-3 and C-4 positions of sugars (Table 1). A lectin classified into Group 4 has not yet been discovered. Recently, the primary structure of lectins has bee It is also classified based on its structure (classification by family) (Table 2).
Table 1 Classification of lectins based on Mäkelä monosaccharide recognition
| Mäkelä classification | origin | Common name for lectin | Carbohydrate binding specificity | mitogenic activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Fuc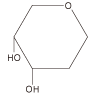 |
gorse | UEA-I | α-L-Fuc | - |
| Gal Gal NAc 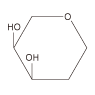 |
soybeans peanuts castor beans _ _ |
SBA PNA RCA120 DBA ABA PHA-E PHA-L |
α-GalNAc>β-GalNAc β-Gal β-Gal α-GalNAc Galβ1-3GalNAc GalNAc GalNAc |
+ ± - - + |
| D-Man D-Glc 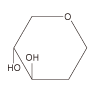 D-GlcNAc |
jack bean pea lentil fava bean |
Con A PSA LCA VFA |
α-Man > α-Glc α-Man > α-Glc α-Man > α-Glc α-Man > α-Glc |
+ + + + |
| pokeweed potato wheat germ gorse |
PWM STA WGA UEA-II |
GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc GlcNAcβ1-4GlcNAc |
+ ± - |
|
| L-Glc L-Man 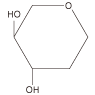 |
- | - | - | - |
Table 2 Classification of lectins by family
| Family (Biodistribution) | sugar specificity | major lectins |
|---|---|---|
| Legume lectin L-type lectin (plant) |
Man Gal Sia Fuc | DSA PHA SBA UEA-I MAM DBA ConA ECA PSA |
| Monocot lectin M-type lectin (plant) |
Mabs | GNA HHA ASA |
| R-type lectin (animal and plant) |
Man Gal Sia Xyl | RCA 120 SSA SNA |
Applications of lectins
The table below shows the relationship between diseases and sugar chains. Recently, many glycoproteins and glycolipids that serve as tumor markers have been discovered. These are produced directly by cancer cells themselves or by surrounding cells under the influence of cancer cells, and their quantitative or qualitative changes are applied to diagnosis. For example, since α-fetoprotein (AFP) increases significantly with liver cancer, quantitative changes have long been used for diagnosis. , it is possible to detect cancer at an early stage. In various diseases including cancer, the discovery of new markers and the development of diagnostic methods using them are eagerly awaited and are being actively researched.
| Diseases involving sugar chains | Marker or target | Change | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| liver disease, liver cancer | α-fetoprotein N-type sugar chain 1) | Increased fucosylated sugar chains Increased LCA binding rate 2) |
Diagnosis by LCA3 ) 4) 5) |
| Transferrin N-glycan | Increased Lex antigen sugar chain6 ) Increased AAL binding rate7 ) |
||
| γGTP N-glycan | Increased branching 8) Increased lactosamine structure |
Early diagnosis of cancer | |
| Cholinesterase N-glycan | Fucose α1-3 increase9 ) 10) | Diagnose with AAL | |
| alcoholic liver disease | Transferrin N-glycan | Decrease/disappearance11 ) 12) | |
| choriocarcinoma | hCG N-glycan | Variation of branching13 ) 14) | Good/Malignant Differentiation |
| rectal cancer | CEA N-glycans15 ) 16) | Type I decreased and type II increased High mannose type increased |
prognosis |
| lung cancer | Lacto-based carbohydrate antigen ganglioside |
Increased sialyl Lea, Lex17 ) GM2 expression18 ) |
|
| stomach cancer, colon cancer | Glycolipids19 ) | ||
| pancreatic cancer | CA19-9 etc. | Increased Sialyl Lea20 ) | |
| Haptoglobin21 ) | Increased fucosylated glycans | ||
| kidney cancer, bladder cancer | Glycolipid | Increased CDH22 ) | |
| Uterine cancer | blood group substance | Expression of H-type sugar chain | Spying in UEA, PNA23 ) |
| prostate cancer | PSA | ||
| ovarian cancer | CA125 | Diagnosis by WGA24 ) | |
| thyroid cancer | Thyroglobulin | Diagnosis at Con A25 ) | |
| myeloma | IgG N-glycan | reduction of galactose | |
| osteosarcoma, osteoporosis | Bone-type alkaline phosphatase sugar chain 26) 27) | ||
| rheumatoid arthritis | IgG N-glycan28 ) 29) α1 -acidic glycoprotein N-glycan30 ) |
Reduction of galactose31 ) | Diagnosis32 ) 33) 34) 35) |
| pancreatitis | in serum | Increased 2-6 Sialyl Lea36 ) | |
| gastritis, enteritis | Glycolipids of mucosal epithelium | ||
| leukemia | Ganglioside | Treatment research37 ) 38) | |
| neuropathy | Ganglioside | therapeutic application | |
| Cataract | Glycolipid | Lex increase39 ) | |
| Alzheimer's disease | Glycolipids40 ) | Increase/decrease in amount of glycolipid |
Literature
- Ohno, M., Nishikawa, A., Taniguchi, N., et al., Int. J. Cancer, 51, 315 (1992)
- Yamashita, K., Taketa, K., et al., Cancer Res., 53, 1 (1993)
- Taketa, K., Clinical Examinations, 39, 1259 (1995)
- Nikkei Sangyo Shimbun, 1997.6.10., P19
- Kuwabara, M., Ariyoshi, Y., Examination and Technology, 27, 443 (1999)
