Suitable for fat staining and quantification of adipocytes
Lipid Assay Kit (Oil Red O staining)
Since adipocytes accumulate neutral lipids in the cells as they mature, the amount of lipid droplets in the cells can be evaluated as an indicator of differentiation.
The Lipid Assay Kit stains adipocytes with Oil Red O stain.
Intended use
- Please use it as an option for the culture series " VAC Visceral Adipocyte ", " Subcutaneous White Adipocyte Culture Kit " and " Brown Adipocyte Culture Kit ".
- Oil Red O staining is one of the methods to confirm differentiation into adipocytes. Oil Red O is a lipophilic red dye that stains intracellular fat globules. This lipid assay kit consists of a cell fixative and an Oil Red O staining stock solution. It stains the fat accumulated in adipocytes, and extracts the dye using an organic solvent to quantify the amount of fat.
Composition
- 2 bottles of 150mL Oil red O undiluted solution
- 2 bottles of 200ml extract
* PMC-AK09F does not contain a fixative (10% neutral buffered formalin).
Please purchase separately or make your own according to the attached manual.
Example of use
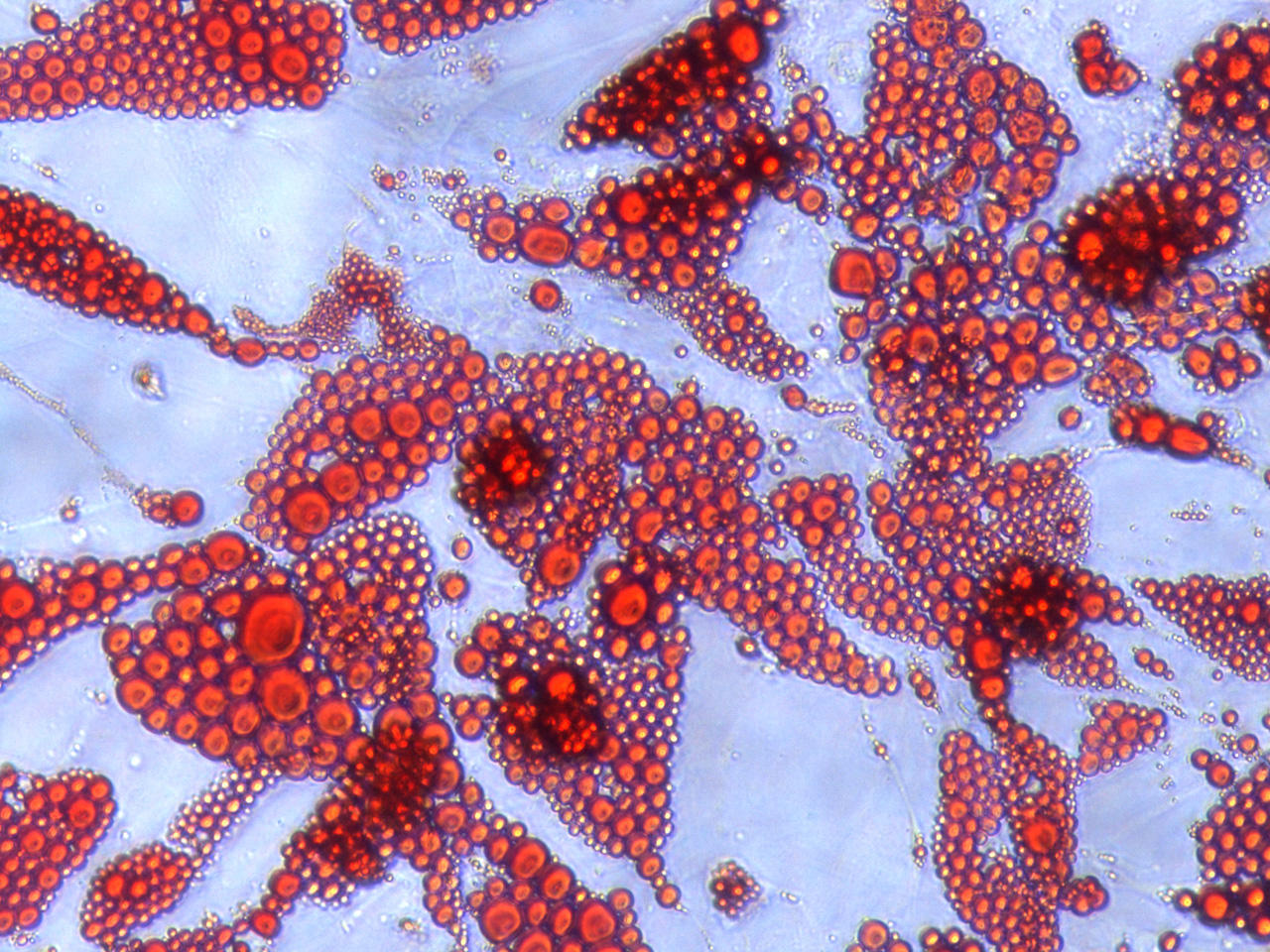
Figure 1 Oillet O staining of human adipocytes
Frequently asked questions and answers (FAQ)
Q: The fixative in the protocol is neutral buffered formalin, but can other fixatives be used?
A: Fixatives other than formalin solutions, especially alcohol-based fixatives, cannot be used because they dissolve fat.
Be sure to use a formalin-based fixative.
Q: Is it possible to shorten the cell fixation time to about 10 minutes?
A: Overnight fixation is recommended, and at least 2-3 hours of fixation is recommended.
If the fixation time is too short, the cell structure cannot be fixed sufficiently and the lipid droplets become fragile, resulting in poor staining.
References
- Tashiro, K., Inamura, M., Kawabata, K., Sakurai, F., Yamanishi, K., Hayakawa, T., Mizuguchi, H.
Efficient Adipocyte and Osteoblast Differentiation from Mouse Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells by Adenoviral Transduction.
Stem Cells. 27, 1802-1811 (2009), (PMID:19544436) - Kawano, S., Maruyama, J., Nagashima, S., Inami, K., Qiu, W., Iwasa, H., Nakagawa, K., Ishigami-Yuasa, M., Kagechika, H., Nishina, H., Hata, Y.
A cell-based screening for TAZ activators identifies ethacridine, a widely used antiseptic and abortifacient, as a compound that promotes dephosphorylation of TAZ and inhibits adipogenesis in C3H10T1/2 cells.
J. Biochem. 158, 413-423 (2015), (PMID:25979969) - Isono, T., Chano, T., Yonese, J., Yuasa, T.
Therapeutic inhibition of mitochondrial function induces cell death in starvation-resistant renal cell carcinomas.
Sci. Rep. 6, 25669 (2016), (PMID:27157976) - Watanabe, Y., Nagai, Y., Honda, H., Okamoto, N., Yamamoto, S., Hamashima, T., Ishii, Y., Tanaka, M., Suganami, T., Sasahara, M., Miyake, K., Takatsu, K.
Isoliquiritigenin Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation in vitro and Adipose Tissue Fibrosis through Inhibition of Innate Immune Responses in Mice.
Sci. Rep. 6, 23097 (2016), (PMID:26975571) - Tanaka, S., Hikita, H., Tatsumi, T., Sakamori, R., Nozaki, Y., Sakane, S., Shiode, Y., Nakabori, T., Saito, Y., Hiramatsu, N., Tabata, K., Kawabata, T., Hamasaki, M., Eguchi, H., Nagano, H., Yoshimori, T., Takehara, T.
Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice.
Hepatology. 64, 1994-2014 (2016), (PMID:27637015) - Shirouchi, B., Kashima, K., Horiuchi, Y., Nakamura, Y., Fujimoto, Y., Tong, LT., Sato, M.
27-Hydroxycholesterol suppresses lipid accumulation by down-regulating lipogenic and adipogenic gene expression in 3T3-L1 cells.
Cytotechnology. 69, 485-492 (2017), (PMID:26983933) - Nakashima, Y., Nahar, S., Miyagi-Shiohira, C., Kinjo, T., Kobayashi, N., Saitoh, I., Watanabe, M., Fujita, J., Noguchi, H.
A Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Analysis of Cells Cultured in DMEM 10% FBS and Chemically Defined Medium Using Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, pii: E2042 (2018), (PMID:30011845) - Nahar, S., Nakashima, Y., Miyagi-Shiohira, C., Kinjo, T., Kobayashi, N., Saitoh, I., Watanabe, M., Noguchi, H, Fujita J.
A Comparison of the Preservation of Mouse Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using the University of Wisconsin Solution and Hank's Balanced Salt Solution.
Stem Cells Int. 2018, 1625464 (2018), (PMID:30258463) - Nakashima, Y., Nahar, S., Miyagi-Shiohira, C., Kinjo, T., Kobayashi, N., Kitamura, S., Saitoh, I., Watanabe, M., Fujita, J., Noguchi, H.
Identification of Proteins Differentially Expressed by Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Immunodeficient Mice.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, pii: E2672 (2019) - Shibahara, H., Ishiguro, A., Inoue, Y., Koumei, S., Kuwayama, T., Iwata, H.
Mechanism of palmitic acid-induced deterioration of in vitro development of porcine oocytes and granulosa cells.
Theriogenology. 141, 54-61 (2020), (PMID:31518729)
| Catalog Number | Product Name | Size |
| PMC-AK09F | Lipid Assay Kit | 1 Set |
