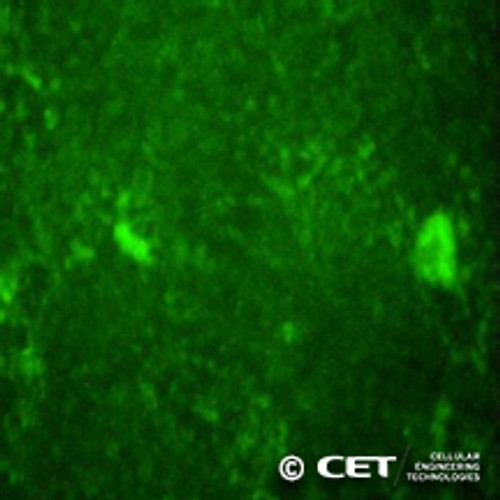
Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells
Cellular Engineering Technologies
- Catalog No.:
- CET-CR1001-500
- Shipping:
- Calculated at Checkout
Human Foreskin Fibroblast-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Line (iPSC)
Our human foreskin fibroblast-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are derived from dermal fibroblast cells and reprogrammed using our patented virus-free, non-integrating episomal DNA method. This cutting-edge technology utilizes a proprietary mix of reprogramming vectors, excluding oncogenic transcription factors such as L-Myc, C-Myc, and Lin28, ensuring a genetically stable and safe iPSC line. These cells offer a powerful model for disease research, tissue regeneration, wound healing, and cell therapy applications.
Our human foreskin fibroblast-derived iPSC line has been thoroughly characterized and validated for pluripotency based on colony morphology, alkaline phosphatase staining, and expression of key pluripotency markers, including SSEA-4. These cells exhibit classical iPSC morphology and robust growth characteristics, making them ideal for differentiation into neural, epithelial, and mesenchymal progenitor cells. We recommend culturing these cells in Human iPSC Growth Media (CET-MR1001-K)
Key Features & Quality Control:
- Pluripotency Validated: Confirmed via colony morphology, alkaline phosphatase staining, and SSEA-4 staining.
- Non-Integrating Reprogramming: Ensures a clean genetic profile without chromosomal abnormalities.
- High Proliferative Capacity: Fibroblast-derived iPSCs exhibit strong growth potential, making them a reliable source for long-term culture.
- Pathogen-Free: Mycoplasma testing confirms sterility and safety.
- High Viability & Secure Shipment: Each vial contains approximately 500,000 viable cells, shipped on dry ice to maintain quality.
Applications of iPSCs:
- Neural Differentiation: Generate neural progenitors and neurons for neurodegenerative disease modeling.
- Hematopoietic Differentiation: Generate blood and immune cell lineages, including erythrocytes, T cells, B cells, and NK cells.
- Epithelial & Mesenchymal Differentiation: Ideal for wound healing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine.
- Toxicology & Drug Screening: Test pharmaceuticals in a human-relevant, fibroblast-derived model.
- Gene Editing & Disease Modeling: Study genetic disorders and develop personalized therapies.
With high genomic stability, strong differentiation potential, and non-integrating reprogramming, our human foreskin fibroblast-derived iPSC line is an essential tool for cutting-edge stem cell research. Order today and advance your research with high-quality iPSCs!
| Documents & Links for Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells | |
| Datasheet | Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells Datasheet |
| Vendor Page | Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells at Cellular Engineering Technologies |
| Documents & Links for Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells | |
| Datasheet | Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells Datasheet |
| Vendor Page | Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells |
| Citations for Human Foreskin Fibroblast iPS Cells – 5 Found |
| Khaiboullina, Svetlana F; Morzunov, Sergey P; Hall, Mark R; De Meirleir, Kenny L; Rizvanov, Albert A; Lombardi, Vincent C. Human dendritic cells transfected with a human papilloma virus-18 construct display decreased mobility and upregulated cytokine production. International Journal Of Oncology. 2013;43(5):1701-9. PubMed |
| Aizman, Irina; Vinodkumar, Deepti; McGrogan, Michael; Bates, Damien. Cell Injury-Induced Release of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2: Relevance to Intracerebral Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Transplantations. Stem Cells And Development. 2015;24(14):1623-34. PubMed |
| Miyashita, Tomoyuki; Omori, Tomokazu; Nakamura, Hiroshi; Sugano, Masato; Neri, Shinya; Fujii, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Hiroko; Tsuboi, Masahiro; Ochiai, Atsushi; Ishii, Genichiro. Spatiotemporal characteristics of fibroblasts-dependent cancer cell invasion. Journal Of Cancer Research And Clinical Oncology. 2019;145(2):373-381. PubMed |
| Miyashita, Tomoyuki; Neri, Shinya; Hashimoto, Hiroko; Akutsu, Asami; Sugano, Masato; Fujii, Satoshi; Ochiai, Atsushi; Ishii, Genichiro. Fibroblasts-dependent invasion of podoplanin-positive cancer stem cells in squamous cell carcinoma. Journal Of Cellular Physiology. 2020;235(10):7251-7260. PubMed |
| Tanaka, Naomichi; Kato, Hidemasa; Tsuda, Hiromi; Sato, Yasunori; Muramatsu, Toshihiro; Iguchi, Atsushi; Nakajima, Hiroyuki; Yoshitake, Akihiro; Senbonmatsu, Takaaki. Development of a High-Efficacy Reprogramming Method for Generating Human Induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) Cells from Pathologic and Senescent Somatic Cells. International Journal Of Molecular Sciences. 2020;21(18) PubMed |