Contrary to the rigid image of bone tissue, bone resorption and bone formation are constantly repeated, and bone remodeling (reconstruction) is constantly taking place. Bone contains two types of cells: osteoblasts responsible for bone formation and osteoclasts responsible for bone resorption . It is known that when osteoclasts are activated and the amount of bone resorption exceeds the amount of bone formation, bone mass decreases and osteoporosis occurs.
Cell / Cell culture products
Osteoclast (human)
Useful for osteoporosis research
Human osteoclasts are induced to differentiate from bone marrow cells to osteoclasts in the presence of M-CSF and RANKL. In addition, by culturing on dentine slices or osteoassay plates at the time of seeding, bone resorption cavities are formed and bone resorption capacity can be evaluated.
Background
Intended use
Osteoclasts are osteoclast precursor cells prepared from human-derived bone marrow mononuclear cells using a selective proliferation method. It has high differentiation efficiency (Fig. 2, 6) and forms clear bone resorption pits in pit formation assay using dentin slices. The ingredients of the separately sold special medium have been adjusted in advance, so you can use it as soon as you receive it.
Experimental example
 |
 |
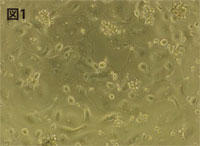
| Figure 1 Human osteoclasts induced to differentiate with M-CSF/RANKL (4 days after seeding) |
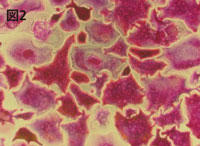
Figure 2 TRAP-stained human osteoclasts |
 |
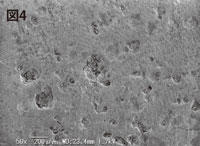 |
| Figure 3. Hematoxylin staining of resorption pit (Pit) on dentin section (2 weeks after culture) |
Fig. 4 SEM image of resorption pit (Pit) on dentin section |
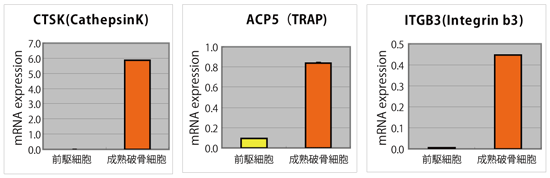
Figure 5
Real Time PCR analysis of major Osteoclast markers (normalized by RPLPO)
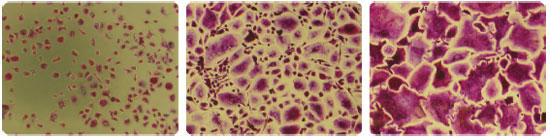 |
||
| 100 μM | 25 μM | 0 μM |
Figure 6 Osteoclast formation inhibition test by addition of β-estradiol
(addition concentration: 100/25/0 μM) TRAP staining on day 5 of seeding
Various assay methods
Dentin slices are suitable for long-term culture as bone models. The easy-to-use Osteoplate Assay allows Kossa staining and TRAP staining on the same surface.
1. TRAP staining method
A marker enzyme for osteoclasts is tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase can be easily detected using the separately sold TRAP staining kit (Part No.: AK04F). (see Figure 8).
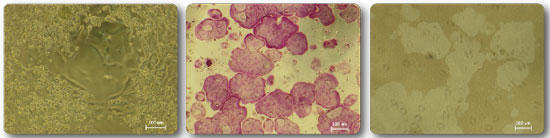
Figure 7 (left) Osteoclasts differentiated with M-CSF/RANKL on the surface of the osteoassay plate Figure 8 (middle) TRAP staining of osteoclasts formed on the surface of the
osteoassay 9 (right) Osteoassay Kossa staining of resorption pits (pits) formed on the plate surface
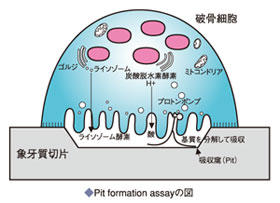
2. Pit Formation Assay method
Osteoclasts formed on dentine slices or osteoassay plates lyse the bone matrix and form resorption pits (pits). Measure total area of resorption pits (see Figures 9 and 10)
Note 1: When using an osteoassay plate, resorption pits (pits) are generally formed after about 5 days of culture, although this varies depending on the seeded cell density and other factors. If the culture period is longer than necessary, all the bone matrix will be absorbed and the resorption pit will not be confirmed.

Figure 10 pH dependence of (pit) formation in dentin slices
3. Human Osteoclast Pit Formation Assay
Measuring device: scanning electrochemical microscope
After culturing human osteoclast precursors on dentin slices (2 weeks), the slices were harvested and sonicated in 5 mL of 1 M ammonia water
to detach the cells. The treated sections were removed from the aqueous ammonia, stained with Mayer's hematoxylin for 1 minute,
washed with water, and dried.
*This measurement uses a specially processed dentin section. Please contact us for more information.
(Measurement example 1)
Shape measurement was performed over a wide area of the formed bone resorption pit.
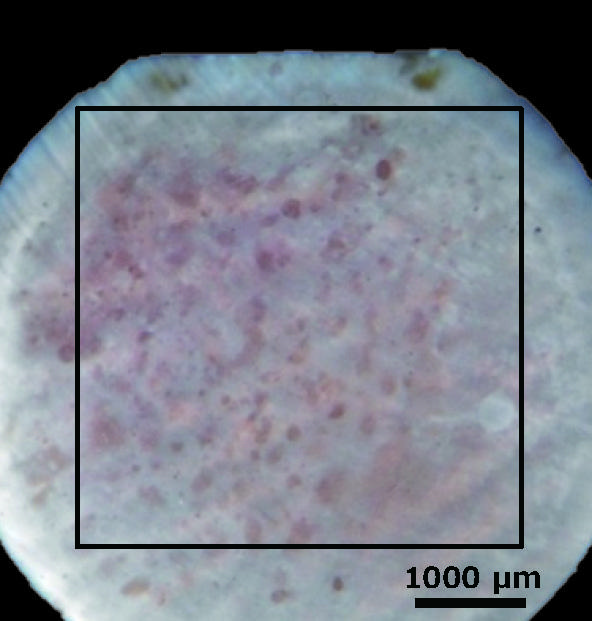
Fig. 11 Rat osteoblasts
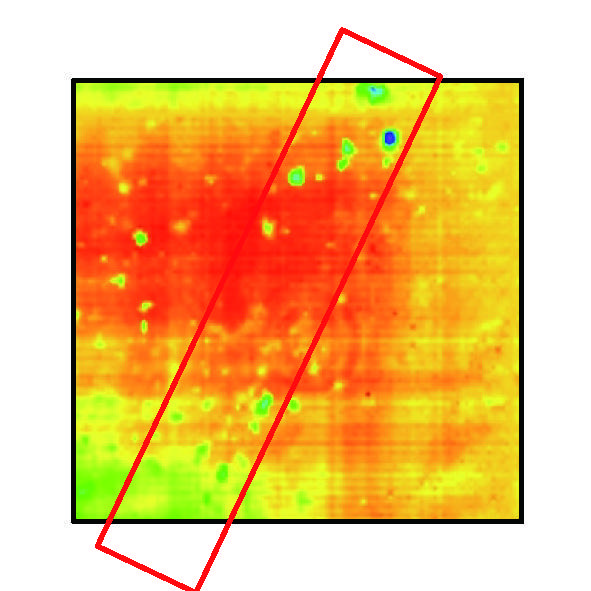
Fig. 12 Measurement result
Furthermore, in order to investigate the details of the bone resorption pits in Fig. 12 □ , we performed high-resolution measurements and analyzed the depth.
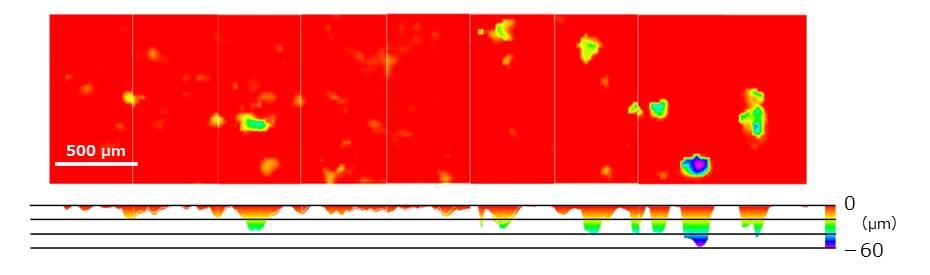
Fig. 13 Results of depth analysis of bone resorption pits
(Measurement example 2)
Similarly, after measuring the shape of the formed bone resorption pit, we extracted the single bone resorption pit shape data and calculated the volume.
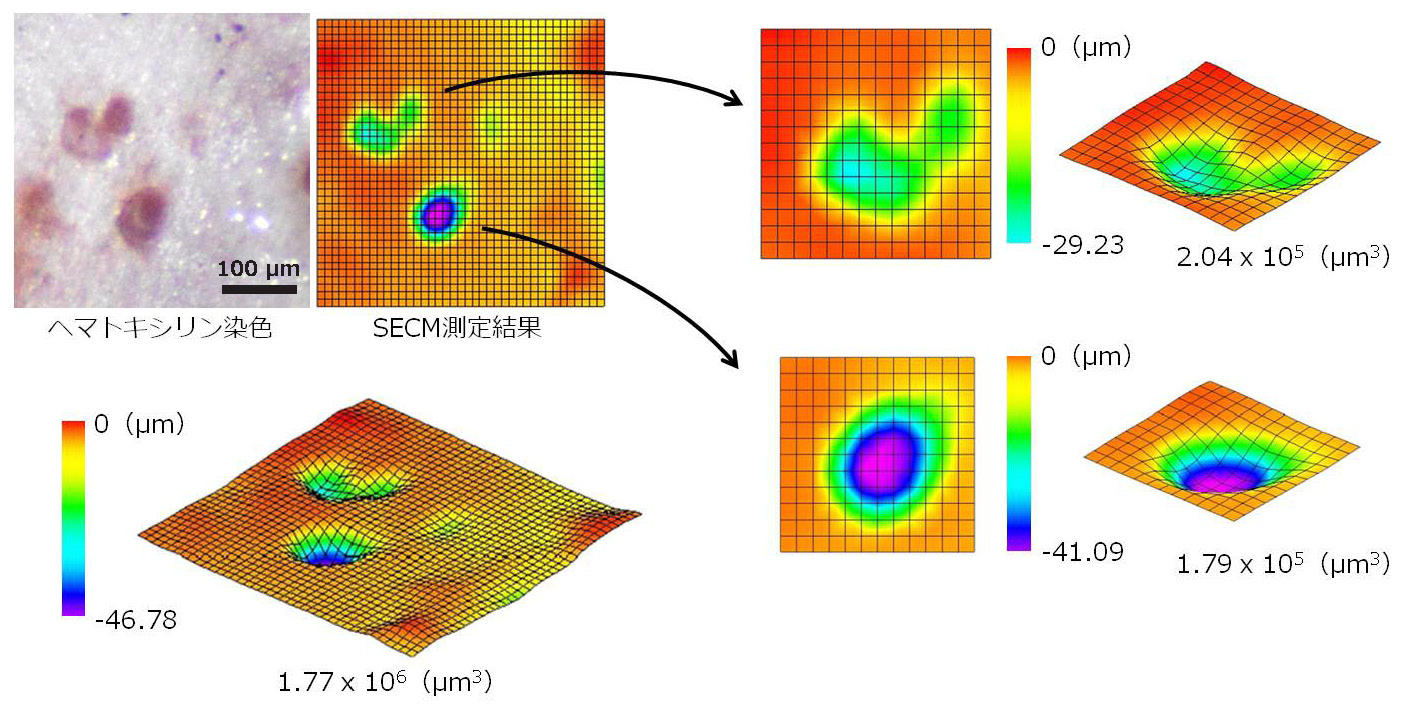
Fig. 14 Volume measurement result of bone resorption pit
|
Product name
|
Catalog number | Size |
| Human Osteoclast / Osteoclast , Human | PMC- OSC15C | 1 VIAL [1.5 x 106 cells] |
